Insights
Written by Melanie Darlington, HR Consultant
1. National Minimum Wage Enforcement and Increases – are you paying the correct amounts?
The Chancellor has announced a £4.3 million yearly increase in the amount available for enforcement of the minimum wage. This money will be used to set up specific teams from HM Revenue and Customs who will target employers most likely at risk of not paying legal rates. The national living wage will be aligned, with the next round of changes taking effect on 1 April 2017. The next increase rates are noted below:
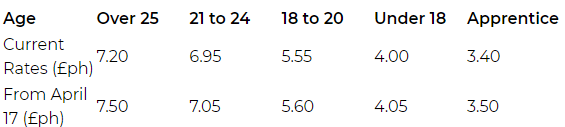
2. Data Protection – data controllers at risk of more severe regulatory fines than data processors for failing to keep personal data appropriately secure. Are you getting prepared?
Although the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) does not come into force until May 2018, the scope of the changes under the new Regulation means that preparations need to be put in place in 2017. Audits need to be completed of employee personal data you collect and what processes you have to ensure that you meet GDPR conditions for employee consent. This new governance on record-keeping requirements means that you will also have to create or amend policies and processes on privacy notices, data breach responses and subject access requests. The GDPR will come into effect before the UK exits the EU and businesses that are not compliant by May 2018 risk fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual worldwide turnover, whichever is higher.
3. Brexit – what affects will it have on your organisation?
Article 50 is set to be triggered by the end of March 2017, which will begin the two year negotiating period to leave the EU. Although no legal changes will take place and Britain won’t leave the European Union in 2017, the continued uncertainty around Brexit has the potential to affect employment and recruitment – especially where employers rely on large numbers of foreign workers.
4. Status and the gig economy – check your staff employment status
In 2016 Uber drivers were decided to be workers rather than self-employed. This may affect your business model and your place amid the ‘gig economy’. The government has launched a review of modern employment to consider how these new models and ways of working are affecting employment rights. If you engage a number of self-employed workers now is the time to discuss this with your HR Consultant to risk assess possible claims for employment rights.
5. Apprenticeship levy – consider your recruitment strategy in 2017
Apprenticeship levy on large employers introduced Employers with an annual payroll of more than £3 million will be required to pay a 0.5% levy on their total pay bill starting on 6 April 2017. This is the government’s initiative to ensure the creation of 3 million apprenticeships by 2020. Employers with an annual pay bill of £3 million and over will:
- Have to pay 0.5% of their pay amount into a digital apprenticeship account
- Receive a £15,000 yearly allowance from the government to offset against this amount, which will be applied monthly
- Have to use the funds within 24 months or they will expire.
Large employers will be able to access levied amounts, plus a government top-up of 10%, to fund apprenticeships from accredited training providers. Smaller organisations that are not required to pay the levy will also be able to receive funding for accredited apprenticeships by contributing 10% towards the cost of an apprenticeship, with the Government paying the remaining cost.
6. Employing Foreign Workers – have you budgeted for the new fees?
Employers sponsoring foreign workers with a tier 2 visa will be required to pay an immigration skills charge of £1,000 per worker (£364 for small employers and charities) beginning in April 2017. The immigration skills charge will be in addition to current fees for visa applications. In April 2017, the minimum salary threshold for “experienced workers” applying for a tier 2 visa will also increase to £30,000. Please consider though that new entrants to the job market and some health and education staff will be exempted from the salary threshold until 2019.
7. Gender pay gap reporting – are your salaries aligned?
The gender pay gap is not the same as equal pay or pay discrimination. The law requiring employers to publish a gender pay gap report will take effect from 6 April 2017.
- The regulations will apply to employers who employ 250 or more employees.
- Employers are required to publish the figures on the organisation’s website and submit evidence of compliance annually to the Government.
- Employers will also need to calculate and publish three other types of figures:
- 1. gender bonus gap
- 2. proportion of men and women receiving a bonus
- 3. proportion of men and women working at each quartile of the organisation’s pay distribution.
The Gender pay gap regulations have yet to be finalised but the deadline for the first report is expected to be 4 April 2018, based on pay and bonus data from 2016/17.
Now is a good time to review and update the following policies to help address any gender pay gap:
- equality and diversity
- enhanced paternity leave and equalised shared parental leave entitlement
- bullying and harassment
- flexible working
- employee development.
8. Benefits of salary sacrifice removed – have your employees been advised?
Employers may need to reconsider their benefit offerings as tax savings through many salary-sacrifice schemes will be abolished from 6 April 2017. The tax advantage will be removed for all salary sacrifice schemes except for the provision of pensions, vouchers, cycle to work schemes, and ultra-low emission vehicles. Schemes in place prior to April 2017 will be protected until April 2018, while arrangements related to cars, accommodation and school fees will be protected until April 2021.
9. Caste discrimination to be introduced – have you considered your employees diversity?
A consultation was announced in September 2016 with the view introduce caste discrimination into the Equality Act possibly from 2017. Caste is a hereditary way of classing an individual’s status based on factors such as their wealth and occupation. It is not explicitly included as a protected characteristic in the Equality Act 2010, however, a recent tribunal case found that ethnic origins, included in the protected characteristic of race, could include questions of descent and therefore caste.
10. Trade union balloting changes – do your Trade Union Agreements need review?
Employers await the implementation date for new balloting requirements under the Trade Union Act 2016. Under the rules, a successful vote for strike action will require a 50% minimum turnout and a majority vote in favour of industrial action. Industrial action in important public services will require a strike vote of 40% of all eligible voters.
If you have any queries in relation to the above, please contact your HR Consultancy team for advice.






